In a world where dystopian narratives often serve as mirrors reflecting the undercurrents of contemporary society, “V for Vendetta” stands out as a profound exploration of sociopolitical themes. Originally conceived as a graphic novel by Alan Moore and David Lloyd, and later adapted into a film, this narrative intertwines elements of totalitarianism, resistance, and ideological conflict. “” delves into the intricate layers of this work, dissecting its commentary on governance, individual freedom, and societal structures. By analyzing the symbolism, character dynamics, and historical parallels within “V for Vendetta,” this article seeks to illuminate the enduring relevance and potent critique embedded in its storyline. As we unpack the narrative’s multifaceted critique of power and oppression, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of its place within the broader context of sociopolitical discourse.
Historical Context and Influences
Alan Moore’s graphic novel “V for Vendetta” is deeply rooted in the sociopolitical climate of the 1980s. The narrative was heavily influenced by the rise of Margaret Thatcher’s Conservative government in the United Kingdom, characterized by its neoliberal policies and strong stance against socialist ideologies. This period saw significant social unrest, with widespread protests and civil disobedience becoming common as the government implemented austerity measures and curtailed civil liberties. The authoritarian regime depicted in “V for Vendetta” mirrors these real-world tensions, portraying a dystopian future where the state exerts oppressive control over its citizens.
Additionally, Moore drew inspiration from historical and literary sources to enrich the story’s depth. Key influences include:
- George Orwell’s ”1984″: A seminal work depicting a totalitarian regime, surveillance, and the suppression of free thought.
- The Gunpowder Plot of 1605: The failed attempt by Guy Fawkes and his conspirators to blow up the House of Lords, symbolizing resistance against tyranny.
- Anarchist Philosophy: The novel explores themes of anarchy as a response to oppressive governance, reflecting Moore’s own political beliefs.
These historical and literary elements coalesce to create a rich, multifaceted narrative that critiques not only the political landscape of the 1980s but also timeless issues of power, control, and resistance.
Themes of Totalitarianism and Resistance
The narrative of V for Vendetta delves deeply into the themes of totalitarianism and resistance, serving as a powerful sociopolitical commentary. The dystopian regime depicted in the story is characterized by absolute control over every aspect of life, employing fear, surveillance, and propaganda to maintain its grip on power. This portrayal highlights the dangers of unchecked governmental authority and the erosion of individual freedoms.
In contrast, the theme of resistance is vividly illustrated through the character of V and his fight against the oppressive state. His actions symbolize the struggle for justice and liberty, embodying the spirit of rebellion against tyranny. Key elements of this resistance include:
- Civil Disobedience: V’s acts of defiance and sabotage challenge the regime’s authority and inspire others to question and oppose the status quo.
- Symbolism: The Guy Fawkes mask becomes a potent symbol of resistance, representing the idea that anyone can rise against oppression.
- Unity and Solidarity: The collective action of the populace, spurred by V’s example, underscores the power of unity in the face of authoritarianism.
Through these elements, V for Vendetta underscores the importance of vigilance and active resistance in the preservation of democratic values and human rights.
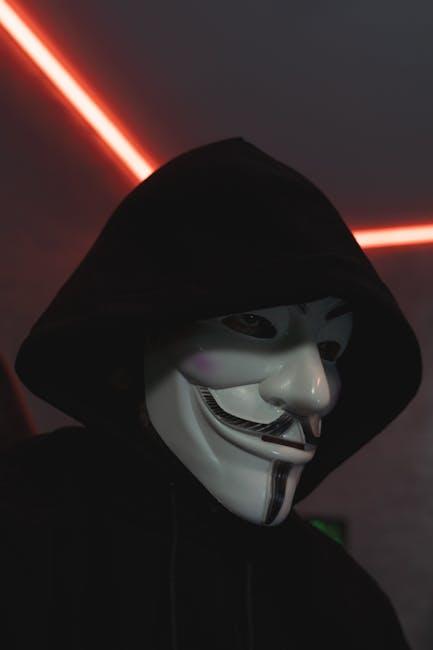

Symbolism and Iconography
The visual elements in V for Vendetta are rife with symbolism and iconography, each meticulously crafted to convey deeper sociopolitical messages. The most prominent symbol, the Guy Fawkes mask, transcends its historical roots to become an emblem of rebellion against tyranny and oppression. Its stark, smiling visage juxtaposed against the backdrop of a dystopian society serves as a powerful reminder of the individual’s potential to challenge authoritarian regimes.
Other notable symbols include:
- V’s Vendetta: The character’s personal vendetta is not just a quest for revenge but a broader critique of fascist control and societal complacency.
- The Red Roses: Frequently used by V, these flowers symbolize both beauty and the transience of life, hinting at the sacrifices required for freedom.
- The Shadow Gallery: V’s hideout, filled with banned art and literature, represents the preservation of culture and intellectual freedom in the face of censorship.
These elements, woven into the narrative, elevate the film beyond a mere action-thriller to a profound commentary on resistance and the power of symbols in shaping political discourse.
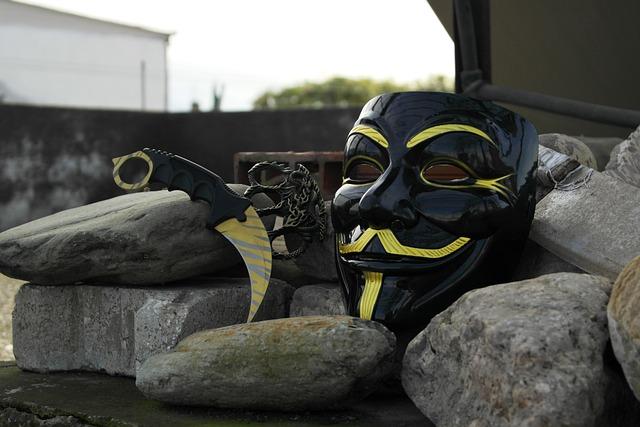

Cultural Impact and Contemporary Relevance
The graphic novel and film adaptation of V for Vendetta have left an indelible mark on popular culture, resonating deeply with audiences across different eras. The iconic Guy Fawkes mask has transcended its fictional origins to become a symbol of resistance and anonymity, widely adopted by activists and hacker groups such as Anonymous. This transformation underscores the story’s powerful commentary on surveillance, authority, and individual freedom.
In contemporary society, the themes explored in V for Vendetta remain strikingly relevant. As governments worldwide grapple with the balance between security and privacy, the narrative serves as a cautionary tale of unchecked power. Key elements include:
- Surveillance: The omnipresent monitoring in the story mirrors current debates over privacy rights in the digital age.
- Authoritarianism: The depiction of a totalitarian regime reflects ongoing concerns about governmental overreach.
- Resistance: The character V embodies the enduring spirit of rebellion against oppression.